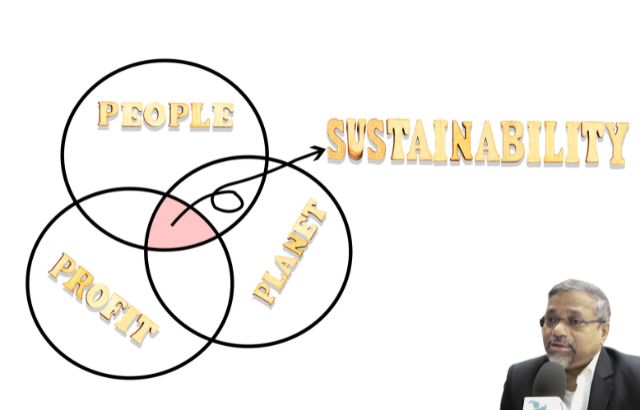
In an era where sustainability has become a crucial focus for businesses and governments alike, the economics of green innovation presents a complex but vital challenge. Striking a balance between profit, environmental impact, and social responsibility is essential for long-term success and positive change. Here’s a closer look at how green innovation can harmonize these three pillars: profit, planet, and people.
1. Profit: The Driver of Innovation
Profit is often the primary motivator for businesses to adopt green innovations. The economic rationale is straightforward: sustainable practices can lead to cost savings, open new markets, and improve competitiveness.
Examples:
- Energy Efficiency: Companies investing in energy-efficient technologies, like LED lighting or advanced HVAC systems, often see substantial reductions in operational costs.
- Waste Reduction: Innovations that minimize waste can lower disposal costs and create new revenue streams from recycled materials.
For instance, Tesla’s push for electric vehicles (EVs) was initially driven by a market opportunity. As the company scaled, it not only contributed to its bottom line but also positioned itself as a leader in sustainable transport.
2. Planet: Reducing Environmental Impact
Green innovation’s primary goal is to mitigate environmental impact. This includes reducing greenhouse gas emissions, conserving resources, and minimizing waste.
Examples:
- Renewable Energy: Solar and wind power technologies provide alternatives to fossil fuels, reducing carbon footprints.
- Circular Economy: Innovations that embrace the circular economy, such as products designed for disassembly and recycling, help reduce waste and resource consumption.
A notable case is Unilever’s commitment to sourcing 100% of its agricultural raw materials sustainably. This initiative not only helps conserve natural resources but also supports biodiversity and reduces the company’s carbon footprint.
3. People: Ensuring Social Responsibility
The people aspect focuses on the social impact of green innovations. This includes fair labor practices, community engagement, and overall societal benefits.
Examples:
- Fair Trade: Green innovations that include fair trade practices ensure that producers in developing countries receive equitable compensation and work in safe conditions.
- Health Benefits: Innovations that improve air quality or reduce toxic emissions contribute to public health.
For example, Patagonia’s dedication to ethical labor practices and environmental advocacy demonstrates how green innovation can positively impact both workers and communities. Their investment in fair labor practices and sustainable materials helps uplift marginalized communities and promotes a healthier environment.
Balancing the Triad: Profit, Planet, and People
Finding the right balance between profit, planet, and people is not always straightforward. Businesses often face trade-offs, such as higher initial costs for green technologies that may impact short-term profitability. However, the long-term benefits often outweigh these challenges.
Strategies for Balance:
- Integrated Strategy: Companies should integrate sustainability into their core business strategies rather than treating it as a peripheral concern. This means setting goals that align with profit motives while also addressing environmental and social impacts.
- Innovation and Collaboration: Collaborating with stakeholders, including suppliers, customers, and community organizations, can lead to innovative solutions that benefit all three pillars. For instance, partnerships for developing sustainable supply chains can enhance both social and environmental outcomes.
- Transparency and Accountability: Transparent reporting and accountability mechanisms help businesses track progress and make necessary adjustments. Sustainable practices should be communicated clearly to stakeholders to build trust and demonstrate commitment.
FAQs on People, Profit, and Planet in Agriculture by Jaiguru Kadam
1. What are the key pillars of sustainability in agriculture?
Answer: The three key pillars are:
- People: Social well-being, including fair wages, health, and education.
- Profit: Economic viability, which focuses on generating sufficient revenue while managing costs.
- Planet: Environmental impact, aimed at reducing emissions, conserving resources, and minimizing waste.
2. How does focusing on “People” impact agricultural sustainability?
Answer: Focusing on people improves social outcomes by ensuring fair labor practices, enhancing community health, and supporting education. This leads to a more equitable distribution of resources and promotes long-term social stability.
3. Why is “Profit” important in sustainable agriculture?
Answer: Profit ensures that agricultural practices are economically viable. It allows farmers and businesses to reinvest in sustainable practices, technology, and innovation. Economic stability is crucial for maintaining continuous improvements and long-term sustainability.
4. What strategies can be used to balance Profit and Planet in agriculture?
Answer: Strategies include:
- Investing in technology: Using efficient irrigation, renewable energy, and sustainable farming practices to reduce environmental impact while improving productivity.
- Cost management: Reducing waste and improving resource use to lower costs and environmental footprint.
- Market alignment: Developing and marketing products that meet consumer demand for sustainability.
5. How can agricultural practices contribute to environmental sustainability (Planet)?
Answer: Practices that contribute include:
- Conservation tillage: Reduces soil erosion and improves water retention.
- Organic farming: Avoids synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, enhancing soil health and biodiversity.
- Crop rotation and diversity: Enhances soil fertility and reduces pest and disease pressures.
6. What role does education and health (People) play in sustainable agriculture?
Answer: Education and health are vital for empowering farmers with knowledge and skills to adopt sustainable practices. Good health ensures a productive workforce and reduces healthcare costs, enhancing overall farm efficiency and well-being.
7. How can farmers increase profitability (Profit) while being environmentally friendly (Planet)?
Answer: Farmers can:
- Adopt precision agriculture: Utilizes technology to optimize resource use and reduce waste.
- Implement sustainable practices: Such as agroforestry or integrated pest management, which can lead to cost savings and higher yields.
- Access subsidies and incentives: For adopting environmentally friendly practices, which can offset initial costs.
8. What are the benefits of integrating social responsibility (People) into agricultural practices?
Answer: Integrating social responsibility leads to improved community relations, better working conditions, and enhanced reputation. It also fosters long-term loyalty among workers and consumers who value ethical practices.
9. How can businesses measure and report on their sustainability efforts?
Answer: Businesses can use sustainability reporting frameworks like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) or Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB). These frameworks provide guidelines for measuring and reporting on environmental, social, and economic impacts.
10. What are some challenges in achieving a balance between People, Profit, and Planet?
Answer: Challenges include:
- High initial costs: Sustainable practices can require significant upfront investment.
- Market fluctuations: Prices for sustainable products can be unstable.
- Complexity: Balancing all three pillars requires integrated strategies and can be difficult to manage effectively.
11. How can small-scale farmers benefit from sustainable practices?
Answer: Small-scale farmers can benefit through:
- Reduced costs: Sustainable practices often lower input costs.
- Increased resilience: Diverse and sustainable farming systems can improve resistance to pests and climate variability.
- Market access: Growing demand for sustainable products can open new market opportunities.
12. Why is it important for large agribusinesses to adopt sustainable practices?
Answer: Large agribusinesses can significantly impact the environment and society. Adopting sustainable practices helps them manage risks, comply with regulations, and meet consumer expectations for corporate responsibility, leading to long-term success and improved brand reputation.
These FAQs highlight the critical aspects of balancing people, profit, and planet in agriculture, offering insights into achieving sustainability in the sector.
Conclusion

The economics of green innovation revolves around the delicate interplay between profit, planet, and people. While the pursuit of profit drives innovation, it must be balanced with environmental stewardship and social responsibility. Successful green innovations not only enhance financial performance but also contribute to a healthier planet and more equitable society. As businesses and organizations continue to navigate this complex landscape, the ultimate goal should be a harmonious integration of all three pillars, leading to a more sustainable and prosperous future for everyone.












