Business Sustainability Analysis : A Tale of Two Farms
On a sunny morning in the rural outskirts of Murbad Taluka, two neighboring farms, Amogh Acres and Greenfields, faced a common problem—dwindling water resources. While both farms cultivated similar crops and shared the same climate, their approaches to sustainability diverged. Amogh Acres embraced modern sustainability practices, while Greenfields continued with traditional methods. As the seasons passed, the differences became starkly evident. Amogh Acres thrived, its crops lush and yields high, while Greenfields struggled with poor harvests.
The success of Amogh Acres wasn’t accidental. It was a product of strategic planning, rigorous analysis, and the integration of innovative green practices. This story isn’t just about two farms; it’s a blueprint for businesses navigating the challenges of sustainability in today’s world. Let’s delve into how tools like SWOT Analysis, GAP Analysis, and the principles of the Green Revolution can transform business operations and drive success.
Business Sustainability Analysis- Understanding SWOT Analysis
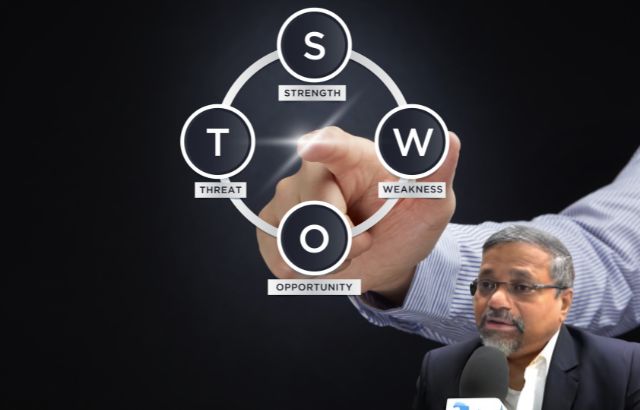
SWOT Analysis—an acronym for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats—is a strategic planning tool that helps organizations identify internal and external factors that could impact their objectives.
Strengths
- Internal Capabilities: Identify unique resources or skills that provide a competitive edge.
- Brand Reputation: Assess the company’s market standing and customer loyalty.
- Financial Health: Examine the financial stability and resources available for investment in sustainability initiatives.
Weaknesses
- Resource Limitations: Pinpoint areas where the organization lacks necessary resources.
- Operational Inefficiencies: Identify processes that need improvement.
- Skill Gaps: Recognize deficiencies in the workforce’s skills related to sustainability.
Opportunities
- Market Trends: Identify emerging trends, such as consumer demand for green products.
- Technological Advances: Leverage new technologies to enhance sustainability.
- Regulatory Incentives: Utilize government incentives for adopting sustainable practices.
Threats
- Market Competition: Consider competitors who may be ahead in sustainability.
- Regulatory Changes: Stay aware of changing laws and regulations.
- Environmental Risks: Address risks related to climate change and resource scarcity.
Business Sustainability Analysis – Unveiling GAP Analysis

GAP Analysis is a methodical approach to compare the current state of a business with its desired future state, identifying the gaps that need to be bridged to achieve those goals.
Steps in GAP Analysis
- Identify Current State: Evaluate the current performance and sustainability practices.
- Define Desired State: Establish clear, measurable goals for sustainability.
- Analyze Gaps: Identify the discrepancies between current practices and desired outcomes.
- Develop Action Plans: Create strategies to bridge the gaps, such as investing in green technologies or training employees in sustainable practices.
The Green Revolution: A Pathway to Sustainability
The Green Revolution refers to a series of research, development, and technology transfer initiatives that significantly increased agricultural production worldwide. In a business context, it emphasizes adopting practices that reduce environmental impact while maintaining profitability.
Key Components of the Green Revolution
- Sustainable Agriculture: Implementing practices that conserve water, reduce pesticide use, and promote soil health.
- Renewable Energy: Transitioning to solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources.
- Circular Economy: Reducing waste through recycling, reusing materials, and designing products for a longer lifecycle.
The Data Behind the Transformation
Agriculture and Water Management
- Water Conservation: Amogh Chemical’s CSR initiatives, such as planting 500 fruit trees and constructing dams, have improved water availability for local farmers, demonstrating a direct link between sustainable practices and resource conservation.
Renewable Energy Adoption
- Global Trends: As of 2023, renewable energy sources accounted for nearly 29% of global electricity generation, with solar power experiencing a 22% increase from the previous year .
- Cost Savings: Businesses adopting renewable energy reported a 20% reduction in energy costs on average .
Circular Economy Impact
- Waste Reduction: Companies that have integrated circular economy principles have seen a 30% decrease in waste production .
- Economic Benefits: The circular economy could generate $4.5 trillion in economic benefits by 2030, highlighting the financial viability of sustainable practices .
Business Sustainability Analysis: Charting the Path Forward

The tale of Amogh Acres and Greenfields serves as a compelling reminder of the power of strategic planning and sustainable practices. By leveraging SWOT Analysis, GAP Analysis, and the principles of the Green Revolution, businesses can not only survive but thrive in an increasingly sustainability-focused world. The journey towards sustainability is not just a strategic choice; it’s a necessity for long-term success and environmental stewardship.
Note :Amogh Acres and Greenfields are imaginary names.












